Consumable Properties
SoloDB features a dynamic property system for consumables that allows for flexible configuration of different types of consumables and their stock. This document explains the concept and structure of the consumable properties system.
Overview
The consumable properties system is built around three key components:
Consumable Types - Define categories of consumables
Properties - Define characteristics that can be applied to consumables or their stock
Application Contexts - Determine where properties can be used (on consumables themselves or on their stock)
Consumable Types
Each consumable in the system has a specific type (e.g., chemical, sheet, resist). The type defines:
Basic information like name and description
Consumption type (percentage, amount, volume, or weight)
Whether it can be used as a substrate
A set of properties that all consumables of this type will inherit
Consumable types serve as templates that define which properties are available for consumables of that type.
Properties
Properties are dynamic attributes that can be associated with consumable types. When a property is associated with a type, all consumables of that type will inherit that property.
Properties have the following characteristics:
Type - Defines the data type and input method (text, number, date, etc.)
Application - Defines where the property can be used (on consumables, on stock, or both)
Label - User-friendly name for the property
Internal Name - System identifier for the property
Default Value - Optional default value for the property
Unit - Optional unit of measurement for the property (e.g., ml, g, %)
Sort Order - Controls the display order of properties
Property Types
SoloDB supports the following property types:
Type | Description |
|---|---|
Text | Free text field |
Radio | Single selection from a list of options |
Date | Date input (no time) |
Checkbox | Multiple selection from a list of options |
Select | Dropdown selection of a single option |
Number | Integer input (no decimals) |
Float | Decimal number input |
Min-Max | Range input with minimum and maximum values |
For Checkbox, Radio, and Select types, you must provide options in the following format:
Where option1 and option2 are the internal codes that will be stored, and Label of Option 1 and Label of Option 2 are the user-friendly labels displayed in the interface.
Application Contexts
Properties can be applied in two different contexts:
Consumable - Properties that describe the consumable itself
Stock - Properties that describe a specific stock transaction (I/O) of the consumable
When creating a property, you can specify where it can be applied:
Only to consumables
Only to stock transactions
To both consumables and stock transactions
This flexibility allows for different properties to be used in different contexts. For example:
A "Manufacturer" property might only apply to the consumable itself
A "Batch Number" property might apply to stock transactions
A "Concentration" property might apply to both
How It Works
Define Properties: Create properties with specific types and application contexts
Associate Properties with Types: Assign properties to consumable types
Create Consumables: When creating a consumable, select its type first
Inherit Properties: The consumable automatically inherits all properties from its type
Set Property Values: Set values for the inherited properties on the consumable
Manage Stock: When adding or removing stock, set values for stock-applicable properties
Example Workflow
Create a property "Concentration" with type "Float" and application "Both"
Create a property "Batch Number" with type "Text" and application "Stock"
Associate both properties with the "Chemical" consumable type
Create a new consumable of type "Chemical"
Set the "Concentration" value for the consumable
When adding stock, set both the "Concentration" and "Batch Number" values
User Interface
Properties are rendered as form elements with labels and help text. Here's an example of a rendered checkbox property:
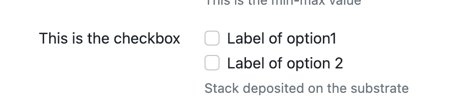
Administration
Properties can be managed via Organisation > Config > Consumable > Properties in the interface. From there, you can:
Create new properties
Edit existing properties
Associate properties with consumable types
Set default values and other property settings